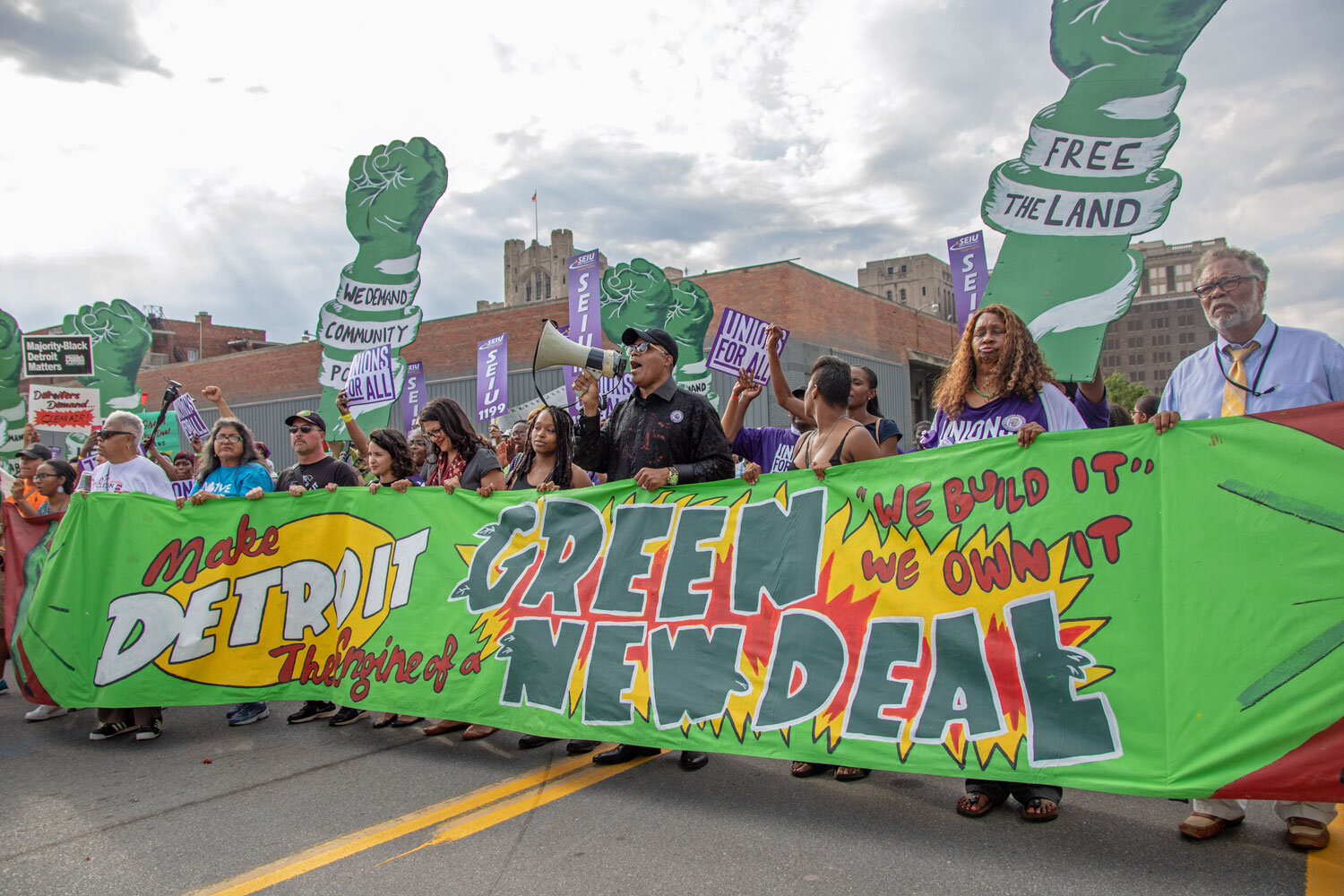

From Progressive Cities to Resilient Cities
Advocates for a Green New Deal forcibly argue that climate action must be racially just and transform institutions that govern social welfare. However, these proposals have focused on cutting carbon emissions and been vague on how the country should adapt to an already changing climate. Early proposals suggest that a Green New Deal for adaptation should emphasize large-scale investments in infrastructure for marginalized communities. But evidence suggests that adaptation infrastructure projects can worsen the well-being of the most vulnerable. For instance, cities tend to prioritize investments for high value real estate or enforce land use and other regulations more stringently on those with less political voice. There also isn’t enough money to protect everyone and every place. Given the prevailing dynamics of urban development, an adaptation moon-shot must go far beyond giving the poor a sea wall or sand dune.

Analyzing Urban Politics
Regime theory has dominated the analysis of urban politics since the publication in 1989 of Clarence Stone’s seminal book, Regime Politics: Governing Atlanta, 1946-1988. As with any influential theory, there have been trenchant criticisms, but for years no alternative approach has emerged to challenge its leading position within the field.

Preserving Education as a Public Good
On October 19, 2017, Bill Gates announced that the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation would invest $1.7 billion in education with 60% going for curricula development and network building among schools, 15% for charter schools, and 25% for “big bets that have the potential to change the trajectory of public education over the next 10 to 15 years.” (quoted in L. Camera, 2017). Less than one month later, on November 16, 2017, the School Reform Commission (SRC), the body set up by the Pennsylvania legislature to govern the Philadelphia School District, voted to dissolve itself, returning school governance to Philadelphia[1] This vote was the result of intense grassroots activism involving thousands of teachers, nurses, school aides, students, parents, and other activists.

Segregation by Design
Jessica Trounstine has recently published Segregation by Design: Local Politics and Inequality in American Cities (Cambridge). A fascinating empirical examination of how local governments have used the distribution of public goods and land use control to increase the wealth of white property owners at the expense of people of color and the poor. This post by Trounstine discusses the core argument of the book and some potential solutions. Her post is followed by several reactions to the book from notable scholars of local and urban politics.
Scholars Exchange: Municipal Takeovers
Municipal takeover policies claim to eschew politics. These policies, which rest on the principle that local government is broken, suspend local democracy in an attempt to fix local fiscal problems. Fear of municipal bankruptcy, economic contagion, and credit downgrades are among the most common motivations for intervening in local municipal affairs. These changes radically rearrange how decisions are made, who has access to decision makers, and, ultimately, who is in power. Many states have adopted or copied municipal takeover policies from each other; as such, when the policies are put in place, we may expect to see similar results or responses from local communities.