
Engaging in Active Learning: Mock Political Campaigns
Teaching Political Science can be extremely content heavy, so it is a struggle to “flip the classroom,” in which the students complete the content material at home in order to have a hands-on experience within the class. I created a group project where the students participate in a mock-political campaign. While this focused on a National Campaign, this could be adapted to a local election context as well. This project aligns with the Student Learning Outcome of students will understand the political process. In order for this group project to be effective, I used weekly scaffolding activities to hold the students accountable. In addition, you should create weekly Student Learning Outcomes that would align with the student understanding a segment of the political process.

Upzoning Chicago
Upzoning—a policy that increases the allowed scale of new construction—has recently attracted considerable attention from policymakers. States from California to Utah are considering legal changes that would require municipalities to increase the amount of new housing allowed to be built in certain neighborhoods. In Minneapolis, local officials have done what was previously thought politically impossible: Allow the construction of multi-family apartments in neighborhoods formerly zoned only for single-family homes.

Private Governance of Public Schools
Charter schools now operate in 43 states and the District of Columbia and their numbers have grown significantly. In most school districts, there are only a handful of charter schools that operate alongside traditional neighborhood-based public schools. However, in 14 urban districts, over 30 percent of the students are enrolled in a charter school. At 93 percent of its public school students in charters, New Orleans tops this list.

Could Housing Crashes Change Voter Preferences?
The election of President Trump in November 2016 came as a surprise to many. Analysts attributed Trump’s election to various factors, such as hostility towards immigrants and racial minorities in white, working class communities that formerly supported Obama and Russian meddling in the election. However, an underexplored factor is the role that the recent housing downturn may have played in the election. There is research showing that Midwestern and Rustbelt counties with a higher percentage of underwater homes (i.e., owing more than the home is worth) were more likely to vote for Trump in 2016 than Romney in 2012.

Voting Can Be Hard, Information Helps
How do voters make decisions about which candidates to support? This isn’t just a question we study as political scientists – it’s a question we confront as voters as well. In 2016, one of us had to vote for a presidential nominee by picking convention delegates on a ballot that did not clearly indicate which presidential candidate each delegate supported. In 2017, another one of us was asked to select 5 names from a list of 13 candidates for town board on a ballot with no additional information about the candidates – not even their party affiliations. In contrast, in both of those years, the one of us living in California chose among candidates – in both partisan and non-partisan races – on ballots including not just names but also “ballot designations” indicating candidate occupations and past experience in the office.

Dealing with Missing Data
In our UAR article, we seek to raise awareness about how to treat missing data in urban studies research. A large proportion of the empirical research on urban politics and policy relies on data collected through surveys of local government or community organization leaders. Surveys provide a relatively efficient way to collect large amounts of consistently measured individual or organizational information needed to conduct comprehensive and accurate statistical analysis. This is particularly important if the aim of research is to produce generalizable findings and contribute to understanding a particular phenomenon by testing theory.
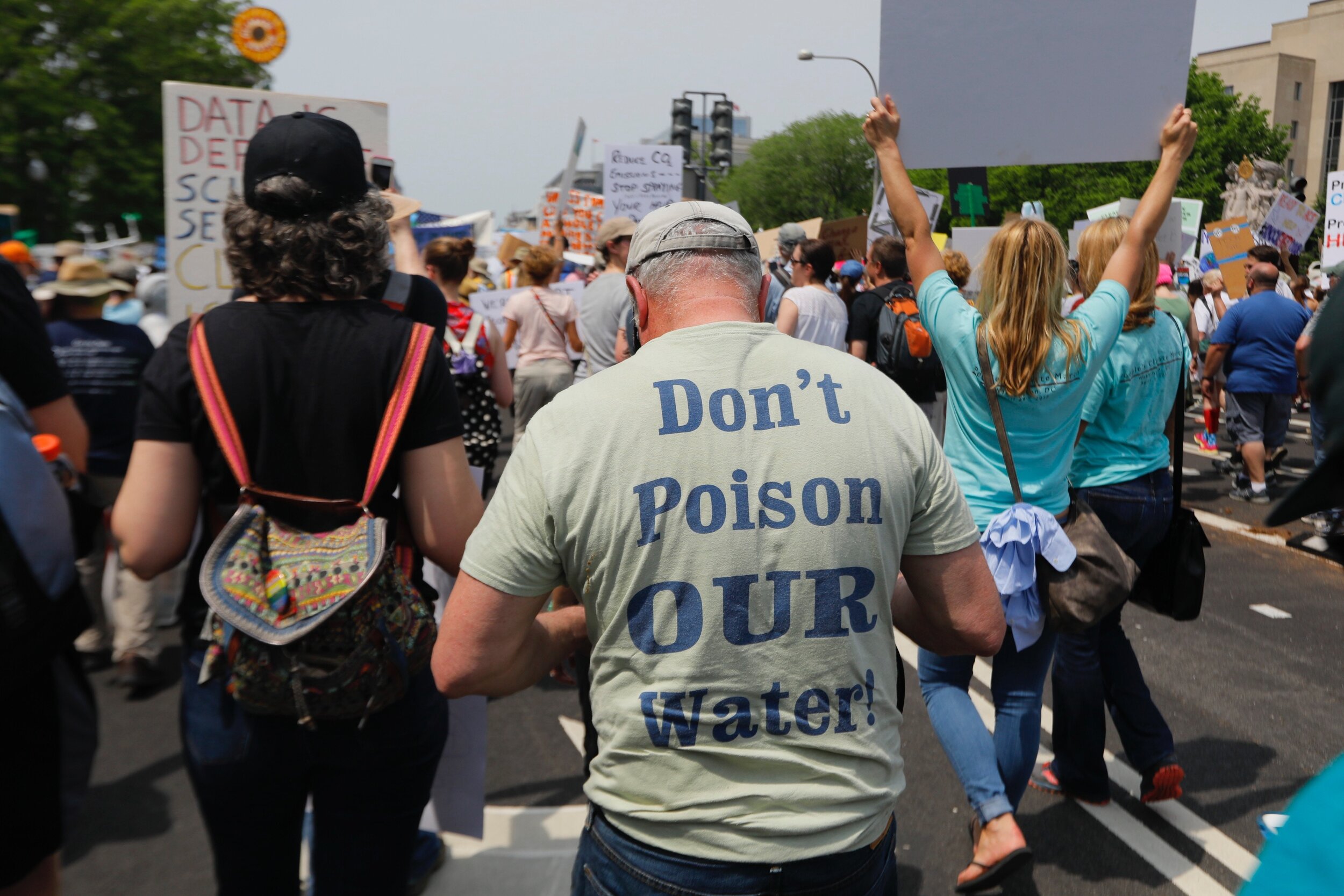
Citizen Partisanship, Local Government, and Environmental Policy Implementation
Early on in the Trump administration, it was clear that the role of the federal government in environmental protection would be lessened, with then Environmental Protection Agency administrator, Scott Pruitt, suggesting that the Trump administration would focus on “cooperative federalism,” emphasizing the role of states in environmental regulation. The developments at the federal level have led scholars and journalists alike to question how this prioritization of state administration in environmental policy will impact implementation.

Factional Voting in Local Elections
Cambridge (MA) is the last of 24 U.S. cities to elect its assembly with the single transferable vote (STV). The point of this system is for a group with, say, 30 percent of votes to end up winning 30 percent of seats — if voters sort into groups. But are voters actually sorting into groups under this STV system? Seventy, fifty, or even thirty years ago, those groups were political parties. As the city became overwhelmingly Democratic, that party system collapsed.

Negotiating the Challenges of Online Learning and Community-engaged Scholarship
There are many benefits to community-engaged scholarship. As academics, we have the opportunity to use higher education as a tool for democracy and a mechanism for enhancing social equity. As educators, community-engaged scholarship can give students “hands-on” experiences and practical skills development. As more programs move toward online curricula, community-engaged scholarship becomes more challenging. It is time consuming, and, if done poorly, might reinforce inequalities rather than promote social equity. Online students come from diverse locations, often work full-time jobs and have family responsibilities, and attend asynchronous classes, none of which lends itself to engaging in community projects.
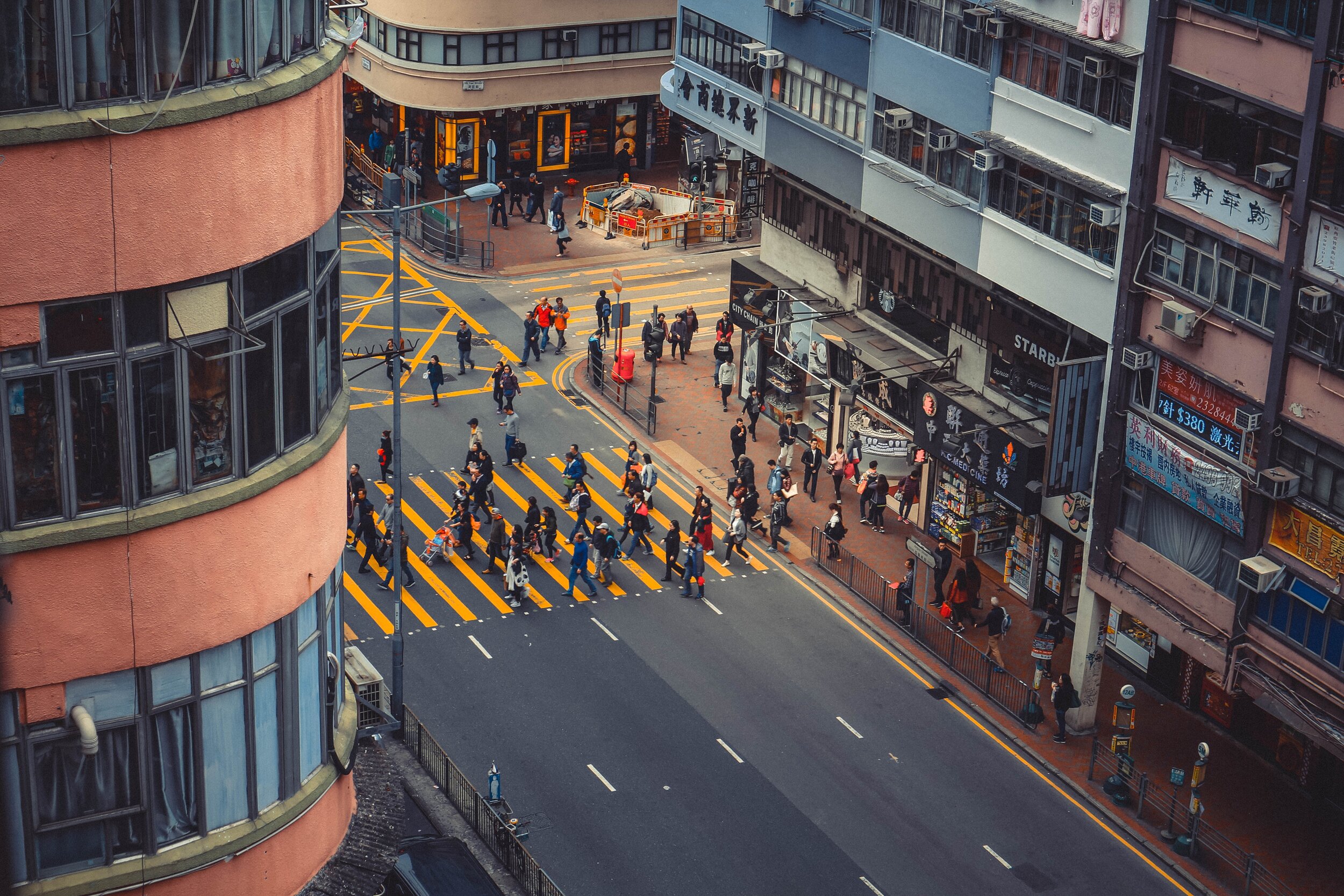

The Changing Urban Political Order and Politics of Space
There is an increasing tension between the land development regime and the grassroots anti-growth coalition in Hong Kong, where public spaces have played a critical role. After the transfer of sovereignty in 1997, Hong Kong's society seemed to decline from prosperous to turbulent, which has aroused public concern in recent years. Many attribute the current dilemma to the regime transition from the British Hong Kong Government to the Hong Kong Autonomous Government and thus conclude that the transitional process of regime change is driven by exogenous factors.

Paving A Path Forward for Engaged Scholarship
Several recent Urban Affairs Review forum pieces have highlighted classroom practices that foster engaged learning by encouraging students, community organizations and policy makers to critically consider and potentially change some of the most complex issues our cities face. But engaged learning, particularly community-based service-learning, can cultivate more than positive communal outcomes. It can be a transformational experience for participants, especially students. In our forthcoming paper at the Journal of Nonprofit and Public Affairs, we lay out a roadmap for designing and executing democratic service-learning courses that generate critical citizenship and social justice advocacy behaviors in public affairs students. Here, we would like to share not only our findings but our process.
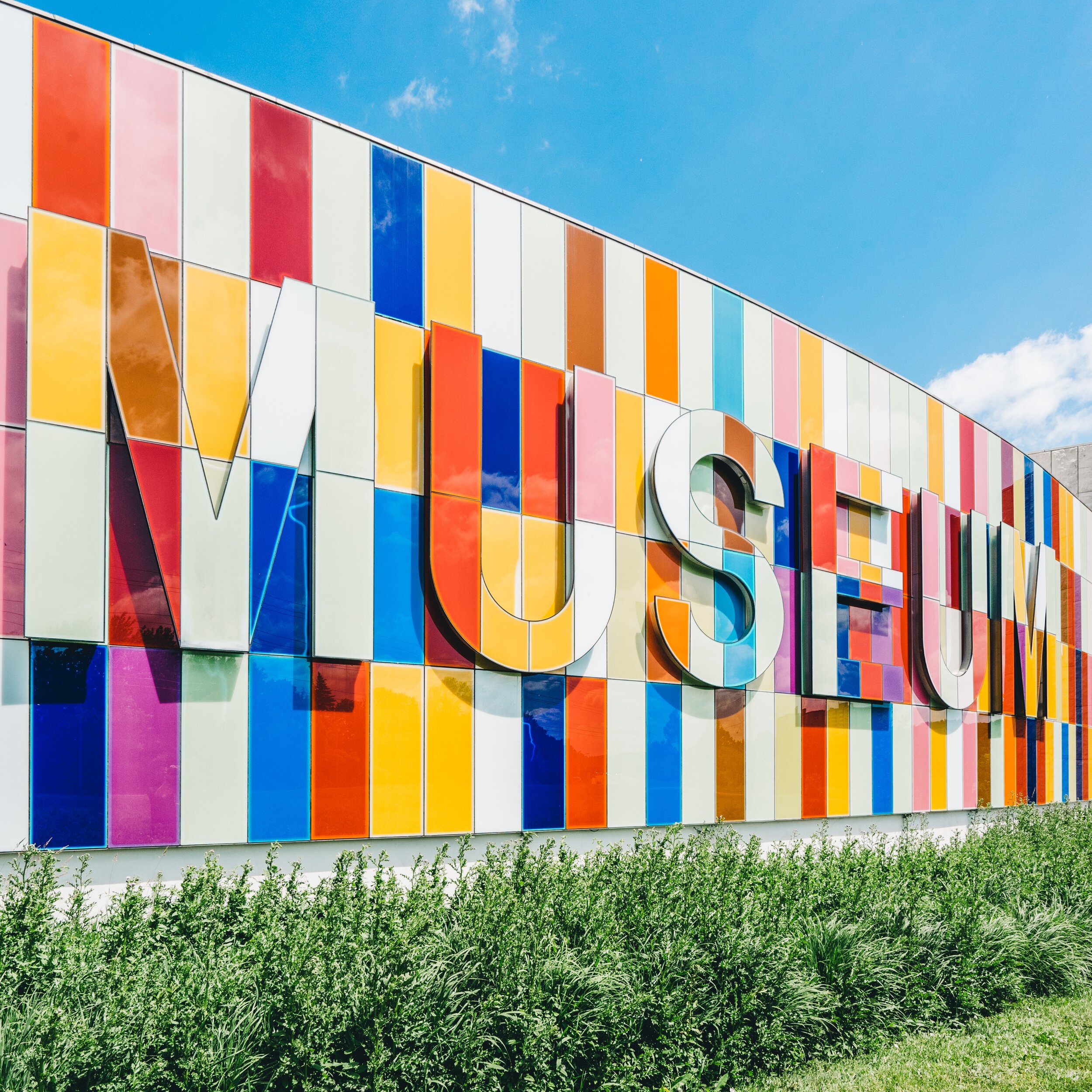

Changing Neighborhoods and U.S. Arts Institutions
Arts institutions, defined as organizations that support art production and consumption space (such as performing arts complexes and museums), have been a popular neighborhood amenity in a variety of cities across the United States. They are believed to improve the livability of neighborhoods and to help attract human capital (highly educated and/or wealthy residents) to their locales. But what effect do they have on differently changing neighborhoods? Do new arts institutions help stabilize neighborhoods losing residents? Do they exacerbate the displacement of vulnerable populations in gentrifying neighborhoods? My research, presented in the UAR article "Changing neighborhoods and the effect of U.S. arts institutions on human capital and displacement between 2000 and 2010,” offers evidence and some answers to these questions.